The rapid evolution of artificial intelligence (AI) in enterprise productivity tools has positioned Microsoft Copilot as a transformative solution for modern workplaces. Organizations across industries are exploring how to integrate AI-powered assistants into daily workflows to enhance efficiency, reduce manual effort, and unlock new opportunities for innovation. However, while Microsoft Copilot promises exceptional productivity gains, success depends heavily on user adoption. Without a structured strategy, even the most advanced AI solutions fail to deliver their intended value.
Adopting Microsoft Copilot is not merely a technical implementation; it is a strategic initiative that requires planning, cultural alignment, and governance. Enterprises that approach this process with a defined framework will accelerate their return on investment and minimize friction. This guide offers a comprehensive roadmap for IT leaders, business stakeholders, and change management professionals to maximize Microsoft Copilot User Adoption effectively.
By the end of this guide, you will have:

Microsoft Copilot is an AI-powered assistant integrated into Microsoft 365 applications, designed to enhance productivity by leveraging large language models such as OpenAI’s GPT in combination with the Microsoft Graph. It operates across multiple Microsoft applications, including Word, Excel, PowerPoint, Outlook, and Teams. The integration enables users to generate content, analyze data, automate repetitive tasks, and summarize complex information directly within familiar workflows.
Unlike traditional automation tools, Copilot adapts to user intent and contextual data. For example:
This deep integration allows organizations to achieve new levels of efficiency. However, realizing these benefits depends on how effectively enterprises enable and support their users in adopting Copilot capabilities.
Microsoft Copilot is more than a feature; it’s a fundamental shift in how work gets done. By embedding AI directly into familiar Microsoft 365 tools, Copilot empowers employees to work smarter, faster, and with greater impact. Organizations that adopt it effectively can achieve:
According to Microsoft’s research on AI productivity, organizations adopting AI tools like Copilot report measurable improvements in operational efficiency and employee satisfaction. However, achieving these outcomes requires overcoming both technical and organizational challenges, which we will explore in the next section.
Employees may view Copilot as a threat rather than an enabler. Concerns include:
Leaders need to implement transparent communication strategies to clarify that Copilot enhances human capabilities rather than replacing them. Clear messaging around Copilot’s role in reducing repetitive tasks and empowering employees to focus on high-value work is critical.
Deploying Microsoft Copilot is not a plug-and-play exercise. It requires:
Failure to address these technical prerequisites can lead to poor user experiences, diminishing enthusiasm for adoption.
Organizations risk operational inefficiencies if they implement Copilot without proper governance. Potential issues include:
A robust governance framework is essential to mitigate these risks and ensure AI adoption aligns with enterprise compliance standards.
Many organizations are already juggling multiple digital transformation initiatives, from migrating to cloud platforms to deploying new collaboration tools. Introducing Microsoft Copilot without a structured change management plan can exacerbate this fatigue, leaving employees feeling overwhelmed and disengaged. When workers perceive every new tool as another disruption rather than an enabler, adoption rates drop significantly. Leaders must position Copilot as an enhancement to existing workflows instead of a completely new way of working to mitigate resistance. By framing the rollout as a value-driven improvement rather than a burden, organizations can reduce change fatigue and foster a more positive adoption experience.
Adopting Microsoft Copilot requires a structured plan integrating technical readiness and change management, ensuring alignment with digital transformation goals.
Adoption Lifecycle Overview
The adoption lifecycle can be summarized in five phases:
Plan → Enable → Train → Measure → Optimize
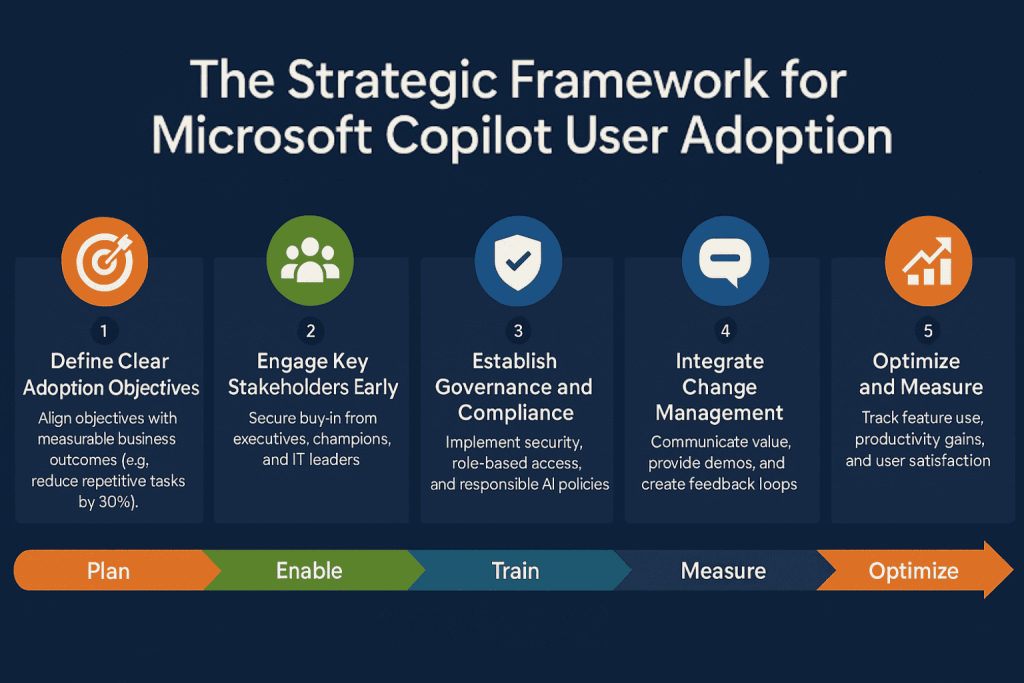
Here’s a strategic framework to guide successful implementation:
Organizations must begin by articulating why they are adopting Microsoft Copilot. These objectives should link directly to measurable business outcomes, such as:
Without clear objectives, adoption becomes reactive, and organizations struggle to measure return on investment (ROI). Aligning Copilot adoption with corporate OKRs (Objectives and Key Results) provides leadership with a tangible way to track progress.
Securing stakeholder buy-in is essential. Stakeholders include:
Establish a governance committee to oversee the option strategy and address potential conflicts. This body ensures that policies, timelines, and resources align with organizational priorities.
Governance must precede rollout. Enterprises should:
Organizations in regulated industries, such as healthcare or finance, should align governance with ISO 27001 standards and local compliance requirements.
Adoption is as much about people as it is about technology. Microsoft recommends aligning with its Adoption & Change Management (ACM) framework. Use structured steps to reduce resistance and improve user confidence. Organizations should:
Communication Plan Outline
Embedding change management principles from frameworks like Prosci ADKAR ensures smoother adoption across all organizational layers.
Post-rollout, analyze adoption metrics and iterate on training strategies:

Organizations must verify that they meet Microsoft’s licensing requirements for Copilot:
Additionally:
Technical readiness ensures that Copilot runs efficiently and securely within the organization’s environment. IT teams should validate the following elements prior to deployment:
Failure to address these readiness factors can lead to degraded performance, security vulnerabilities, and user frustration, ultimately hindering adoption.
Copilot’s value multiplies when it becomes a natural extension of the organization’s digital workplace strategy. This involves ensuring compatibility and smooth integration with existing workflows and tools:
A well-prepared technical foundation minimizes disruptions during rollout, accelerates user adoption, and maximizes the return on investment in Copilot.
Technical enablement alone does not guarantee adoption. Employees must understand how to use Copilot effectively to realize its full value. Comprehensive training programs address this need.
Traditional training methods such as generic webinars or static documentation often fail to deliver lasting impact because they lack immediacy and context. Modern learning approaches should prioritize embedded, task-oriented education. For instance:
This strategy minimizes friction, accelerates skill acquisition, and creates a smoother onboarding experience. By allowing employees to learn in the flow of work, organizations reduce the likelihood of resistance and improve long-term engagement.
A one-size-fits-all training model does not work for diverse organizational roles. Instead, companies should implement customized learning paths that align with job functions and daily responsibilities:
Tailored learning paths ensure relevance, which increases adoption speed and reduces the cognitive load on employees.
Copilot is an evolving tool, with frequent feature updates and enhancements. Consequently, training should not be treated as a one-time event but as a continuous process. Enterprises can achieve this through:
These measures reinforce confidence, keep employees engaged, and prevent stagnation in tool adoption.
Finally, effective training strategies must be data-driven. Organizations should leverage analytics to measure impact and identify areas for improvement:
This ongoing feedback loop ensures that training remains relevant, efficient, and aligned with business goals, ultimately maximizing the return on investment in Copilot.
DAPs like VisualSP enable organizations to bridge the gap between technical implementation and user proficiency. They provide:
By incorporating a DAP into the Microsoft Copilot adoption strategy, organizations create a support ecosystem that drives continuous learning, mitigates resistance to change, and ensures employees fully leverage Copilot’s capabilities.
Adoption metrics focus on user engagement with Microsoft Copilot features. Key points include:
Regulatory bodies are introducing frameworks for responsible AI usage, and organizations cannot afford to remain passive. The EU AI Act, for example, sets out risk-based requirements for AI applications, which enterprises must integrate into their compliance strategies. Similar guidelines are emerging globally, from U.S. executive orders to Asia-Pacific data protection standards. These regulations will require transparent documentation of AI decision-making processes and robust risk assessment protocols. Preparing for these changes early will reduce disruption when compliance becomes mandatory.
Microsoft will continue to expand Copilot capabilities beyond Microsoft 365, integrating features across platforms like Dynamics 365 and Azure-based services. New functionality, such as predictive analytics and industry-specific Copilot models, will further enhance enterprise value. Organizations should adopt an iterative approach to training and governance, anticipating feature rollouts rather than reacting to them. Establishing a continuous improvement cycle ensures that employees remain equipped to leverage new tools effectively. This proactive stance transforms adoption into an ongoing journey rather than a one-time initiative.
The future of enterprise productivity will not be limited to a single platform. As organizations adopt multiple AI assistants across various ecosystems, interoperability will become a critical success factor. Businesses will need strategies for integrating Microsoft Copilot with tools from vendors such as Salesforce, Google Workspace, and industry-specific platforms to ensure seamless workflows. Standardizing governance policies and data-sharing protocols will minimize security risks while enabling consistent AI experiences across applications. Companies that invest early in interoperability planning will position themselves to scale AI adoption efficiently without creating operational silos.
While the strategic framework outlines the high-level path to successful Copilot adoption, many organizations, especially midsize businesses, need a clear, actionable roadmap to get started quickly. With limited resources and an urgent need for measurable results, these companies benefit from a simple, phased approach that translates strategy into daily execution. The following 30-60-90 day playbook provides a practical guide to help midsize organizations move from planning to tangible outcomes in a structured and accelerated way.
Microsoft Copilot is showing up across the Microsoft 365 suite, but for many midsize organizations, it’s not showing results. The technology is here, but the return on investment (ROI) only materializes when employees actually use it.
So, how do you turn Copilot from shelfware into a productivity game changer?
The adoption lifecycle we discussed earlier provides a high-level roadmap for enterprise-scale deployment. However, organizations, especially midsize firms, also need a tactical playbook to drive immediate results on the ground. The following section introduces the 3A Framework (Awareness, Activation, Adoption) and a 30-60-90 Day Plan to operationalize Copilot adoption quickly and effectively.
Copilot adoption hinges on one powerful framework:
Many companies mistakenly pursue complex, expensive AI initiatives before nailing the basics. The result? Frustration, delays, and shelfware. Organizations often jump into ambitious, high-cost AI projects without first addressing foundational needs. These large-scale initiatives may promise innovation but frequently lead to delays, budget overruns, and low adoption. By focusing instead on practical, ready-to-use solutions like Microsoft Copilot, companies can achieve faster wins, lower risk, and measurable impact. Starting simple ensures momentum and builds confidence before scaling more complex AI efforts.
Two Paths to AI Adoption
| Heavy AI (High Effort, High Risk) | Microsoft Copilot (Practical AI, Out-of-the-Box) |
|---|---|
| Build custom models | Available in the tools you already use (Word, Outlook, Teams, Dynamics) |
| Develop purpose-built agents | No extra build - just learn how to ask |
| Large consulting + engineering budgets | Immediate time savings (day 1 wins) |
| Long timelines (months/years) | Employees cherry-pick improvements to daily work |
| High risk of failure / shelfware | Scales organically across teams |
For midsize organizations, success hinges on practical strategies that deliver immediate, measurable impact rather than large-scale moonshot projects.
The effectiveness of Microsoft Copilot largely depends on the quality of the prompts users provide. Vague or overly general requests often yield incomplete or unhelpful results, while clear, specific, and well-structured prompts lead to more accurate and actionable outputs. Teaching employees how to craft effective prompts is essential to unlocking Copilot’s full potential. Building a shared library of proven prompts can accelerate learning, improve consistency, and drive faster value across the organization.
Using Copilot effectively starts with better prompts. Here’s a simple but powerful shift:
Train users to be prompt-savvy. Even better—create a shared prompt library so everyone benefits from what works.
Prompts are the new playbooks. Sharing them accelerates adoption at scale.
Successful adoption of Microsoft Copilot requires more than just turning on a feature. A phased approach helps ensure that awareness, training, and impact build progressively across the organization. The 30-60-90 day plan offers a structured roadmap that starts with identifying key use cases, moves into activation and user engagement, and culminates in broader adoption and measurable results. This framework provides a clear timeline for organizations to transition from initial rollout to sustained value.
Days 0–30: Establish the Baseline
Days 31–60: Drive Activation
Days 61–90: Scale and Sustain
To demonstrate the tangible value of Microsoft Copilot, it is essential to analyze real-world use cases where productivity gains directly translate into financial savings. By examining common scenarios such as sales reps reducing prep time or finance teams accelerating reporting cycles, organizations can clearly quantify Copilot’s return on investment. These examples show how even modest time savings, when scaled across teams and repeated over time, can result in substantial cost reductions and operational efficiency.
Sales Team
Finance Team
Multiply across functions, and the financial impact becomes undeniable.
Adopting Microsoft Copilot is more than turning on an AI feature within Microsoft 365; it is a strategic initiative that impacts workflows, governance, and organizational culture. Success requires a holistic approach that combines technical readiness, robust governance frameworks, and comprehensive user enablement strategies. Without these elements, even the most advanced AI solution can fail to deliver its intended value.
The most effective adoption plans go beyond initial rollout and focus on sustainability. This involves creating clear objectives, aligning stakeholders, integrating change management principles, and leveraging tools like Top Digital Adoption Platforms to provide real-time guidance. Equally important is measuring impact through well-defined metrics covering adoption rates, productivity improvements, and employee experience to ensure the organization continuously improves its strategy.
Microsoft Copilot represents a transformative step in the evolution of workplace productivity. Organizations that commit to thoughtful planning and structured adoption will unlock their full potential, enabling their teams to work smarter, faster, and with greater confidence in an AI-driven future.
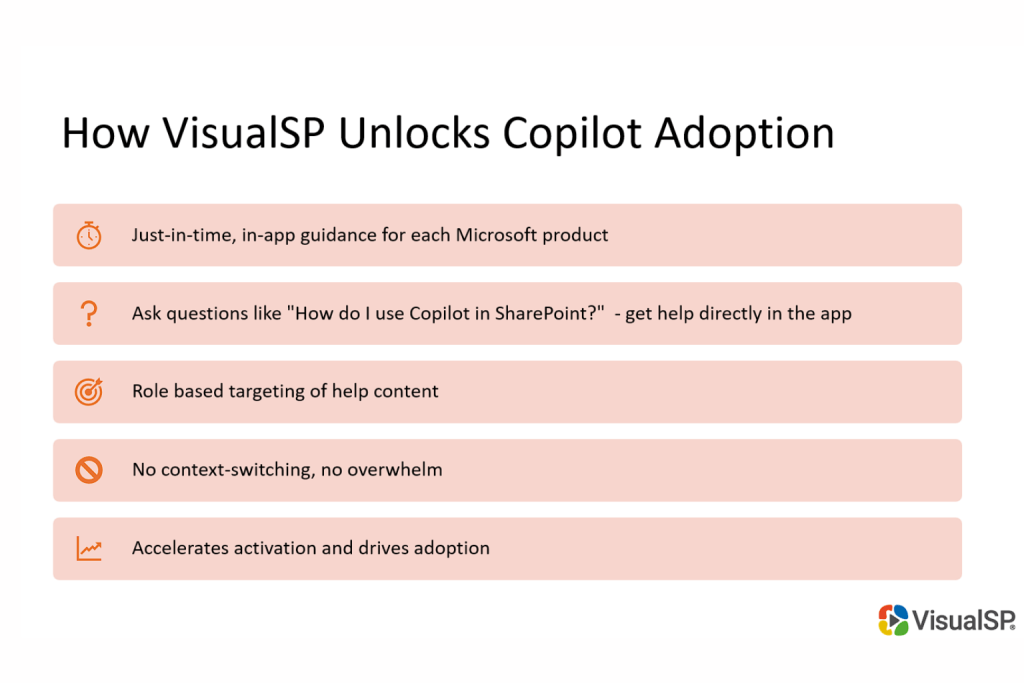
Implementing Microsoft Copilot successfully requires more than technical configuration. It demands a comprehensive strategy that addresses change management, governance, and user training. This is where we at VisualSP can make a significant difference. Our platform is purpose-built to drive digital adoption by providing just-in-time, in-app guidance and AI-powered support within the applications your employees already use every day, so there’s no context-switching, no overwhelm.
VisualSP integrates seamlessly with Microsoft 365, including Teams, Word, Excel, and other enterprise tools, to deliver:
By leveraging VisualSP, organizations accelerate activation and drive adoption of Microsoft Copilot without overwhelming users or IT teams. We help reduce support costs, boost productivity, and ensure compliance, all while creating a positive employee experience.
Three Actions to Take This Quarter
Fuel Employee Success
Stop Pissing Off Your Software Users! There's a Better Way...
VisualSP makes in-app guidance simple.