
When I look at the accelerating pace of workplace transformation, a clear pattern emerges across every industry. Organizations are being pushed to operate with greater precision, faster execution, and more intelligent use of information. The teams that thrive are the ones that learn to extend their capabilities through new tools and more effective ways of working.
Microsoft Copilot has become central to that evolution. It does not replace professional expertise. It strengthens it. For those who learn to use it well, Copilot becomes a powerful multiplier that accelerates analysis, improves communication, and removes much of the friction that slows modern work.
This article is written for practitioners who want to move beyond basic usage and develop the deeper Copilot Skills that produce measurable impact in technical environments, operational workflows, and strategic decision-making. The goal is to provide a comprehensive and practical roadmap that aligns with the realities of enterprise work today, where AI-assisted productivity is no longer optional but essential for achieving meaningful results.

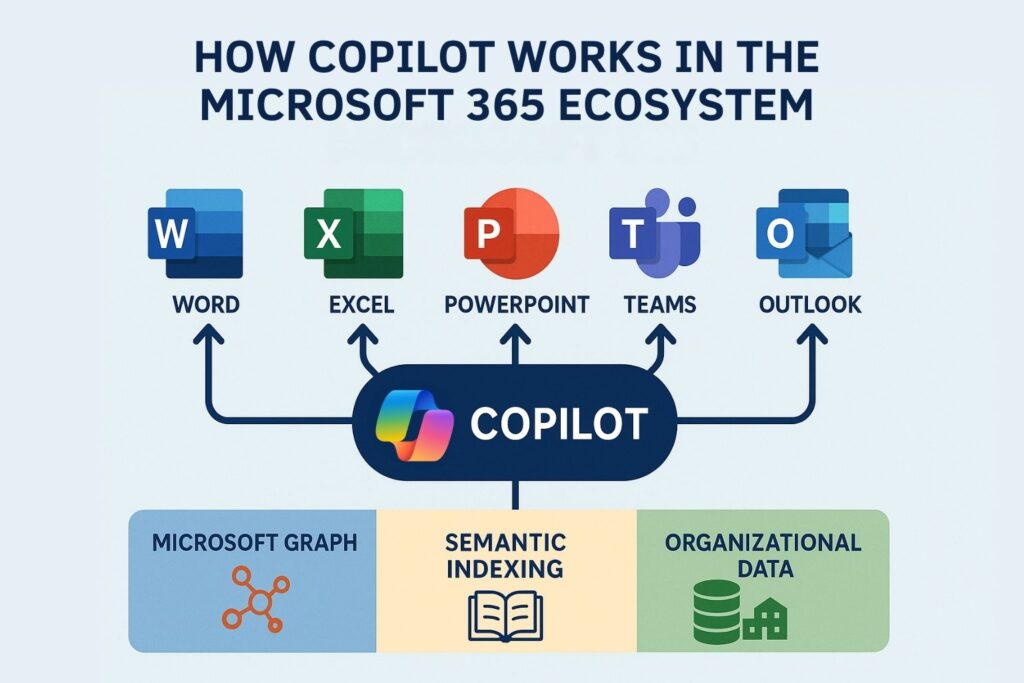
Professionals who want to develop strong Copilot Skills must first understand the structure and logic behind the Microsoft Copilot ecosystem. Copilot functions as a multilayered intelligence system that spans across Microsoft 365 applications, the Microsoft Graph, and an organizational data environment. Each component contributes to how Copilot interprets intent and generates its outputs. This means users who appreciate the architectural mechanics gain a definitive advantage because they know how to frame prompts that align with the system’s capabilities.
Copilot operates as an orchestrated pipeline that blends large language models with enterprise data access. The experience may feel like a simple chat interface, but underneath it lies a sequence of evaluation, retrieval, grounding, filtering, and generation. The better professionals understand this sequence, the more precisely they can craft inputs that produce consistent and accurate responses. Strong Copilot Skills rely on this foundational architectural literacy.
The Copilot architecture uses models from the GPT family in combination with Microsoft’s internal orchestration frameworks. These frameworks decide how queries should be grounded in enterprise data, whether the prompt requires data retrieval, and which information sources are appropriate based on user permissions. The process does not rely solely on the model’s internal knowledge. Instead, the system uses a structured retrieval process that takes advantage of the Microsoft Graph to identify relevant files, messages, events, or datasets.
The architecture evaluates the user’s prompt, then determines which elements of the prompt require contextual enrichment. If the user references a meeting, document, or project, the orchestrator retrieves relevant data and provides that context to the model. This produces responses that are consistent with organizational realities rather than generic assumptions. This architecture also includes compliance, auditing, and logging layers to ensure responses align with corporate accountability requirements.
Microsoft Graph is the backbone of Copilot because it unifies all enterprise content, identity objects, SharePoint libraries, Teams conversations, and other digital assets into a single navigable structure. Copilot queries the Graph to identify related content, user relationships, and historical activity. Semantic Indexing enhances this by reorganizing enterprise content into an optimized format for AI retrieval. This process allows Copilot to understand relationships such as project sequences, version histories, and recurring collaboration patterns.
Professionals with advanced Copilot Skills recognize that high-quality output depends on the quality and organization of their digital environment. Disconnected files, outdated repositories, or poorly structured knowledge assets reduce Copilot’s effectiveness. Conversely, well-organized digital content significantly improves accuracy, relevance, and response quality.
The Copilot ecosystem spans across Microsoft 365 applications, each tailored to a different kind of work:
Understanding how each application integrates with Copilot helps professionals use the right skill in the right context. Strong Copilot Skills involve recognizing which Copilot instance is best suited for a particular task, whether it is analytical, communicative, or organizational.
Mastering Copilot Skills involves more than writing simple commands or generating formatted text. In this article, the five foundational skills reflect capabilities that accelerate day-to-day work across nearly every role in the enterprise. These skills also scale into advanced workflows involving data analysis, documentation, cross-team communication, and rapid knowledge synthesis. When professionals practice these skills through structured repetition, they develop a form of operational literacy that enables Copilot to act as a reliable assistant in complex environments.
The five foundational Copilot Skills include:
Summarization is one of the most powerful Copilot Skills because modern workplaces generate overwhelming amounts of information. Professionals must evaluate strategic documents, project updates, policy materials, customer communications, and meeting transcripts. Manually reading each source consumes time that could be spent on deeper analysis or strategic planning. Copilot enables users to turn long content into clear summaries that highlight essential points and eliminate unnecessary detail.
How Copilot Summarization Works
When users request a summary, Copilot evaluates the structure of the input, identifies thematic clusters, and extracts relevant concepts. The model identifies key decisions, major arguments, risks, dependencies, and actionable next steps. It also examines contextual clues such as section headings, timestamps, conversation threads, or formatting signals. This helps produce summaries that reflect the true intent of the source material.
Professionals can modify the scope and focus of summaries by specifying what matters most. They can ask for summaries focused on performance metrics, stakeholder concerns, customer issues, or technical risks. The more specific the prompt, the more tailored the output becomes.
Practical Applications of Summarization
Summarization supports a broad range of use cases across roles and industries. Professionals use it to evaluate complex artifacts in a fraction of the time it would take to read them fully. Scenarios where summarization provides immediate value include:
These applications demonstrate how Copilot Skills directly contribute to better decision-making and operational clarity.
Benefits of Mastering Summarization
Professionals who master this skill improve their ability to manage workload complexity. They can review more content in less time without sacrificing comprehension. They can also use summaries as conversation starters with stakeholders, allowing them to validate or refine interpretations quickly. This reduces uncertainty, accelerates cycles of feedback, and ensures that teams align around shared understanding.
Effective communication is a critical differentiator in professional environments. Tone, clarity, structure, and audience alignment determine whether a message lands successfully. Copilot supports communication excellence by transforming text to match specific stylistic or tonal requirements. Professionals who master this skill produce communications that feel polished, intentional, and tailored to their stakeholders.
Adjusting Formality for Professional Audiences
Communicating with executives requires a different level of formality compared to communicating with peers or external partners. Copilot can adjust sentence structures, vocabulary, and rhetorical cues to produce messages that fit the expected communication norms. This enables professionals to quickly adapt content for different audiences without having to manually rewrite messages.
Controlling the Length of Communications
Long messages can overwhelm readers. Copilot supports length control by expanding short notes into full narratives or condensing extended content into brief, actionable summaries. This helps professionals communicate more efficiently while respecting the time constraints of stakeholders.
Length transformation is especially valuable when preparing:
Adapting Content for Different Stakeholders
Every audience has unique expectations regarding detail, terminology, and framing. Copilot can rewrite content for technical teams, non-technical stakeholders, customers, partners, or leadership groups. The system adjusts the depth of explanation, level of jargon, and overall narrative to match the intended audience. Strong Copilot Skills include knowing what each stakeholder needs and creating content that aligns with that profile.
Professionals frequently gather information in raw formats such as bullet lists, shorthand notes, checklist items, or meeting observations. Turning these inputs into formal deliverables often requires time-consuming rewriting and formatting. Copilot eliminates much of this effort by transforming structured or semi-structured inputs into complete documents.
Converting Notes Into Structured Documents
Meeting notes often capture only the essential points, but they lack the structure needed for official communication. Copilot reads these notes and produces well-organized documents with clear sections, logical flow, and professional formatting. This accelerates the process of creating project updates, design proposals, requirement documents, or post-meeting summaries.
Expanding Bullet Lists Into Detailed Content
Bullet lists are quick to create but can be challenging to share in formal business environments. Copilot expands bullet lists into full paragraphs or multi-section documents that convey the necessary context. This helps teams move from ideation to documented plans without manual rewriting.
Turning Tables Into Narrative Reports
Structured data, such as tables, requires narrative interpretation to support decision-making. Copilot analyzes trends, identifies comparisons, and explains the significance of each data point in simple language. This is particularly valuable for scenarios involving performance reviews, financial updates, or operational reporting.
Excel remains one of the most widely used analytical tools in enterprise settings. Copilot significantly enhances Excel by allowing professionals to explore data using natural language. This makes advanced analysis accessible without requiring complex formulas or scripting.
Identifying Trends With Copilot
Copilot reads datasets and identifies key trends across time periods, categories, or segments. It highlights high-growth regions, declining segments, cyclical patterns, or emerging indicators. Professionals gain immediate insight into what the data reveals, even when working with large or complex sheets.
Detecting Anomalies and Outliers
Anomalies often signal important events such as system failures, customer behavior shifts, financial discrepancies, or operational risks. Copilot identifies unusual values and explains why they matter. This supports faster escalation and more accurate tracking.
Generating Plain Language Insights
Not all decision makers understand raw numbers or Excel structures. Copilot supports communication by converting numerical patterns into plain language explanations. This bridges the gap between analytical teams and strategic stakeholders.
Modern work often breaks down not from poor strategy but from poor coordination. Meetings are overrun, follow-ups get lost, and actions are delayed. Copilot in Microsoft Teams transforms how teams collaborate by organizing agendas, capturing discussions, and tracking commitments in real time. Professionals who master this skill create more focused interactions and maintain better project momentum across distributed teams.
Drafting Structured Agendas
Most professionals enter meetings with loosely defined objectives. Copilot changes this by helping to generate structured agendas based on the meeting's purpose, history, and participant roles. It suggests topics, sets time allocations, and aligns agenda items with prior discussions. This creates clearer expectations and better time management for every meeting.
This agenda generation works particularly well when:
Capturing Discussion Highlights
Capturing what happened in a meeting can be more difficult than conducting the meeting itself. Copilot listens during Teams meetings and compiles a structured summary, including key decisions, differing viewpoints, unresolved questions, and immediate outcomes. This ensures teams don’t waste time repeating prior conversations or revalidating what was already agreed.
Professionals can refine the prompt to highlight:
Tracking Action Items With Ownership
Teams often leave meetings with a vague sense of what the next steps are. Copilot helps by generating a list of action items tied to participants, due dates, and dependencies. This ensures that follow-up doesn’t rely solely on human memory. Tasks can be easily exported to Planner, To-Do, or project tracking tools with minimal effort.
Professionals who adopt this Copilot Skill reduce friction across sprints, handoffs, and asynchronous coordination. They spend less time on admin work and more on high-value execution.
Before moving into advanced techniques, professionals can strengthen their foundational Copilot Skills through a short, hands-on exercise. This mini-lab is designed to help users experience the impact of the five core skills in real work scenarios.
Choose a sample document, meeting transcript, email thread, or dataset that reflects your actual daily challenges; something you would normally need to summarize, rewrite, analyze, or convert into a formal deliverable.
Write a prompt that applies one of the five core skills to your selected material.
Examples include:
Run the prompt in Copilot and review the generated output. Evaluate how effectively Copilot applied the skill, where clarity improved, and where additional context might enhance the result.
If used in a team or training setting, compare outputs, discuss variations, and refine prompts collaboratively. This group critique helps participants understand how different inputs influence quality and teaches repeatable prompting patterns.
This mini-lab reinforces practical mastery of the five foundational skills and builds user confidence before progressing to more advanced Copilot capabilities.
The foundational Copilot Skills form the baseline, but power users can extend their capabilities with advanced methods. These include prompt engineering techniques, workflow chaining, and platform integrations across the Microsoft ecosystem. Professionals who move beyond the basics unlock more automation, creativity, and insight from the platform.
Prompt engineering is the practice of designing structured inputs that guide Copilot to generate optimal results. In professional environments, prompts often include roles, formatting instructions, structured thinking patterns, or reasoning sequences. This is especially useful for complex documents, nuanced analysis, or audience-specific content.
Effective techniques include:
These patterns create repeatable results and reduce the variability of Copilot’s responses.
Enterprise tasks often span multiple applications. For example, a user might summarize an Excel dataset, use the output in a Word document, then generate a PowerPoint presentation from the Word draft. Each handoff introduces complexity. Copilot enables fluid transitions across apps when users adopt consistent prompts and build sequential tasks.
A typical flow might include:
These multi-app flows help users consolidate steps that were previously fragmented across teams or tools.
Power users and developers can design their own Copilot workflows using Power Automate and Copilot Studio. These tools allow professionals to:
By creating these tailored assistants, organizations embed Copilot Skills into their internal operations, making AI an integral part of their infrastructure rather than a standalone layer.
Individual proficiency is valuable, but enterprise transformation requires team-wide Copilot adoption. Organizations need a structured plan to build, distribute, and sustain Copilot Skills at scale. This involves designing playbooks, aligning workflows, and embedding enablement mechanisms into day-to-day systems.
Different roles demand different usage patterns. A finance analyst uses Copilot to detect anomalies, while a recruiter uses it to draft candidate summaries. Playbooks give each role a curated set of prompts, examples, and best practices. They provide guardrails and accelerators for employees navigating real work challenges.
Each playbook should include:
This structured enablement improves the consistency and confidence of users across business functions.
Formal training is not sufficient for long-term behavioral change. Professionals need just-in-time assistance when using Copilot in real workflows. Embedding micro-support like tooltips, inline examples, or contextual videos directly inside Microsoft 365 tools significantly improves adoption. These aids must appear in the moment of need, without breaking user flow.
This approach works best when:
Prompt examples embedded in Outlook, Excel, or Word help users take the next step without confusion or delay.
Prompt reuse is an underappreciated aspect of Copilot Skills. Once users refine an effective prompt, it becomes a reusable asset. Sharing these prompts through internal communities or repositories boosts collective intelligence. Teams can iterate together, test new variations, and gradually improve Copilot’s value across the organization.
Some best practices include:
Organizations that document and disseminate prompt knowledge scale AI faster and more effectively.
Tracking Copilot usage isn’t just about frequency; it’s about depth, diversity, and outcome quality. Metrics should cover:
These indicators highlight where skill development is working and where support is needed.
Quantitative metrics must be paired with qualitative feedback. Professionals can share how Copilot accelerated decision-making, reduced backlog, or improved documentation quality. These stories provide context for the numbers and validate the return on investment.
Feedback can be collected through:
A healthy feedback loop encourages continuous experimentation and refinement.
Organizations benefit from categorizing their user base into maturity levels based on Copilot usage. This helps tailor learning paths and investments. A sample maturity model might include:
This framework helps organizations move beyond adoption to long-term transformation.
AI will continue to evolve, and with it, the demands on professionals to adapt their Copilot Skills. Future interfaces may involve voice, spatial computing, and the coordination of self-directed agents. Today’s skillset must expand to prepare for a world where Copilot is always on, always available, and always learning.
In the future, Copilot won’t be a single assistant but part of a network of agents. One Copilot might summarize a client meeting, another generate pricing models, and a third draft a proposal, all in sequence. Professionals must learn how to define goals across these agents and review the combined output.
Copilot is not just a command tool. It is becoming a proactive digital colleague. It will suggest improvements, offer preemptive warnings, and manage routine tasks. Professionals will need to develop judgment skills around AI output: when to trust it, when to override it, and how to collaborate with it at scale.
Many enterprises will design their own internal Copilots using platforms like Azure OpenAI and Microsoft Copilot Studio. These internal assistants will carry specialized knowledge, workflows, and datasets. Professionals must know how to work with, test, and optimize these custom agents as part of their role.
In today’s workplace, Copilot skills are no longer optional. They are becoming a core part of modern knowledge work. The ability to summarize complex information, improve communication, generate content, analyze data, and coordinate team activities is now a baseline requirement for professional productivity. As AI tools grow more advanced, these skills will separate high-performing individuals and organizations from those that fall behind.
Building these skills at scale requires more than casual experimentation. It demands structure, ongoing support, and a culture of shared learning. For teams focused on operational excellence, the next step is to integrate Copilot skills directly into everyday workflows so they become second nature, just like any other core business competency.
At VisualSP, we’ve seen firsthand how organizations struggle not just with adopting powerful tools like Microsoft Copilot but with enabling their people to use them effectively, consistently, and responsibly. Developing Copilot Skills across an organization doesn’t happen by accident. It requires real-time support, contextual learning, and scalable guidance embedded directly where work is being done.
That’s exactly where VisualSP comes in.
Our digital adoption platform integrates seamlessly into enterprise applications like Microsoft 365, SharePoint, Dynamics, and your custom tools. With VisualSP, your users get instant, in-the-flow help through guided walkthroughs, inline tips, embedded videos, and AI-powered prompt libraries. There’s no need to search documentation or submit support tickets. The help they need appears right where they need it, when they need it.
What sets us apart is our AI-powered content generation. You can instantly create support materials such as walkthroughs and in-app prompts that align with your specific Copilot use cases. This not only accelerates rollout but ensures that guidance remains relevant and effective as workflows evolve.
VisualSP is designed with enterprise readiness in mind. We offer secure, compliant implementations with no compromise on user experience. Our platform is trusted by more than 2 million users globally, including teams at NHS, Visa, and VHB. Whether you’re rolling out Microsoft Copilot across departments or refining the AI strategy for your business, VisualSP gives you the infrastructure to make that adoption successful.
If your organization is investing in AI but struggling to translate potential into productivity, let’s solve that gap together.
Start enabling Copilot Skills at scale with VisualSP. Contact us today to discover how we can support your transformation from the outset.
Fuel Employee Success
Stop Pissing Off Your Software Users! There's a Better Way...
VisualSP makes in-app guidance simple.