
Client relationship management remains the linchpin of professional services success. Over the past decade, I have witnessed a dramatic transformation in how organizations track, nurture, and expand their client relationships. The question I often hear from clients and colleagues alike is deceptively simple: Can Microsoft Office really serve as a client relationship management system? As an expert in digital transformation and digital adoption, I’ve evaluated this scenario from multiple angles, including technical architecture, organizational change management, and user adoption. This article aims to unpack that question with clarity, nuance, and the level of depth you expect as a fellow professional.
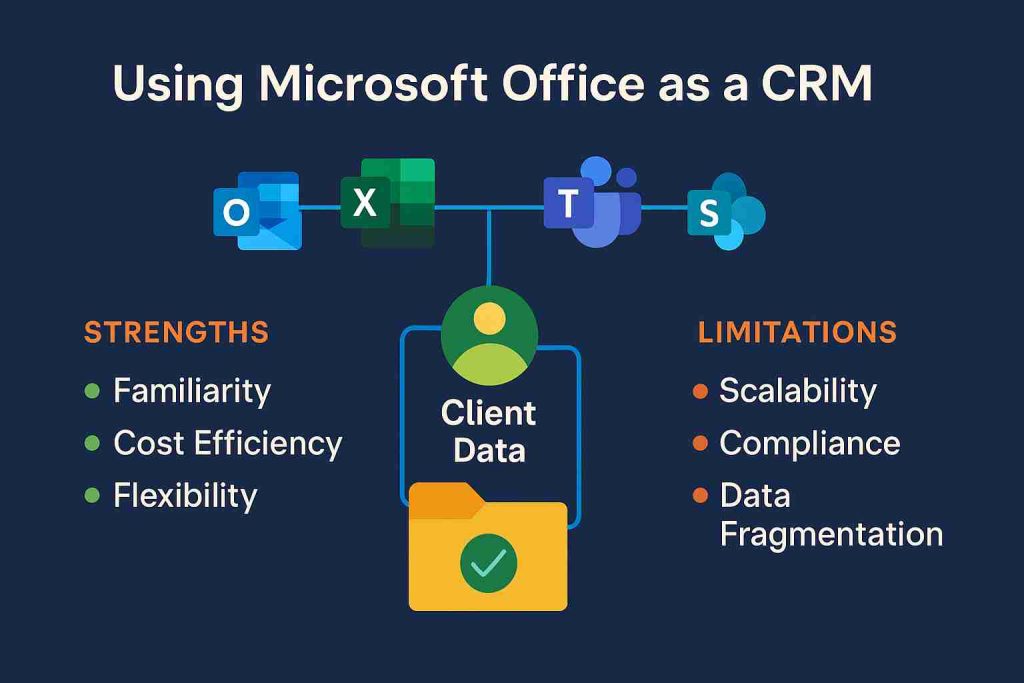
Over time, I’ve seen professionals gravitate to Microsoft Office because it feels accessible. The familiarity of Excel sheets and Outlook inboxes offers a comforting illusion of control. Yet, the convenience of these tools can obscure their inherent limitations when scaled for sophisticated client CRM requirements. A spreadsheet might track names and notes, but it lacks relational architecture. Email folders can archive conversations, but cannot model complex workflows or deliver analytics comparable to an enterprise-grade client management system.
Before committing to Office as your client management CRM, consider whether its architecture aligns with your business complexity. Microsoft client relationship management through Office requires not only technical configuration but also disciplined governance and user training. While you can cobble together workflows across SharePoint, Teams, and Power Automate, these solutions demand continuous oversight. I’ve encountered many firms that underestimated the cumulative burden of maintaining such setups, eventually opting for purpose-built CRM platforms to regain efficiency and data integrity.
Modern CRM platforms have transformed far beyond basic contact management. They serve as unified systems of record, connecting client interactions with sales pipelines, support activities, and project delivery milestones. A robust CRM for client management includes structured workflows that ensure consistency in every phase of the engagement cycle. Role-based permissions and configurable dashboards support accountability and transparency across departments. These capabilities have become standard expectations in industries where client relationship management is a strategic priority.
Artificial intelligence is redefining how CRM systems deliver value. Predictive scoring models can analyze historical data to identify clients most likely to renew or disengage. Natural language processing capabilities enable professionals to query client records conversationally and generate reports without manual data manipulation. These insights improve prioritization and support more proactive decision-making. AI also drives recommendations for next-best actions, improving client outcomes and efficiency. Modern CRM tools are increasingly expected to embed these capabilities natively.
Regulatory requirements have expanded in both scope and complexity over recent years. Frameworks such as GDPR, HIPAA, FINRA and mandate secure data handling, detailed audit trails, and client consent management. Organizations must demonstrate the ability to control access to sensitive information and respond to compliance inquiries promptly. CRM systems now include built-in controls to support these obligations, minimizing the need for manual recordkeeping. Maintaining compliance without these tools requires considerable operational discipline and oversight.
Client engagement occurs across email, social media, chat, phone calls, and in-person meetings. Modern CRM systems consolidate these interactions into a single, unified timeline that provides context for every touchpoint. This centralization enables consistent messaging and faster response times, improving the client experience. Disconnected systems often create information gaps that lead to duplicated efforts or missed opportunities. Data unification also supports more comprehensive analytics and forecasting.
Several trends are shaping CRM development in the current decade. The shift to remote and hybrid work environments has amplified the need for cloud-based tools accessible from any location. Automation has reduced reliance on manual processes, improving accuracy and speed. Low-code configuration options have democratized system customization, empowering non-technical professionals to build tailored workflows. Mobile-first design principles have become standard to support work on the go. These trends continue to influence how organizations evaluate CRM technology.
Microsoft Office includes an array of applications widely adopted in professional environments. Outlook manages email, calendaring, and contact storage. Excel provides spreadsheets for data analysis and simple databases. SharePoint offers collaboration spaces and document management. Access allows the development of relational databases for more structured data models. Teams supports chat, conferencing, and persistent collaboration channels. Each application contributes different components relevant to client relationship management.
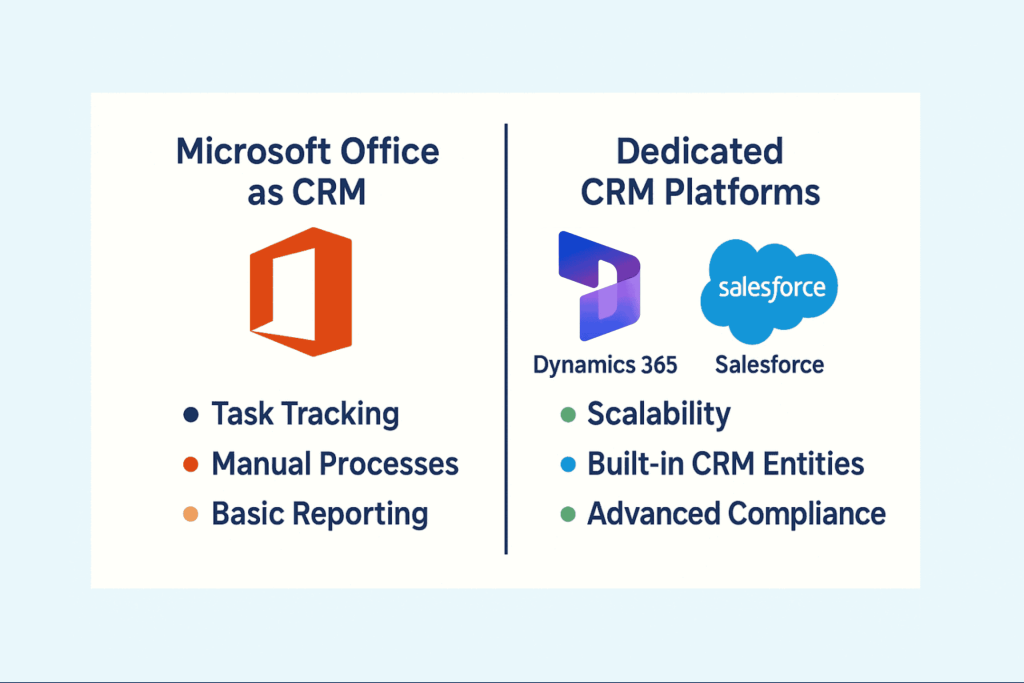
Microsoft Office fundamentally differs from Dynamics 365, which is designed as a comprehensive CRM and ERP platform. Dynamics 365 includes preconfigured entities for leads, opportunities, and cases, along with workflow automation and compliance capabilities. Office lacks these features by default and relies on manual setup and integration to approximate them. This distinction often becomes critical when organizations try to scale client management practices. Dynamics 365 offers capabilities that align more closely with modern CRM expectations.
Microsoft Office benefits from seamless integration across the broader Microsoft environment. Azure Active Directory manages authentication and security policies for all applications in the suite. Power Platform tools, including Power Automate and Power BI, extend functionality through automation and analytics. SharePoint and Teams interoperate to enable document sharing and collaborative workflows. This interconnected foundation reduces barriers to consolidating information across tools. Integration can improve user productivity if configured carefully.
Many organizations believe that combining Office applications creates an effective CRM solution by default. This perception often underestimates the complexity involved in designing and sustaining consistent workflows. Office applications are not designed to support relational data models in the same way that CRM platforms do. Relying on manual processes and disconnected data sources increases the likelihood of inconsistency and errors. Clear planning is necessary to avoid unintended gaps in client relationship management capabilities.
Microsoft Office tools can deliver essential client management functions for small teams or simple engagement models. As the scale and complexity of operations increase, limitations become more pronounced. Excel’s concurrency issues and SharePoint’s performance thresholds can create bottlenecks that impede productivity. Manual governance becomes unsustainable when data volume grows beyond a certain threshold. Recognizing these constraints is essential to avoid operational disruption.
Outlook functions as the communication hub for many professional teams. It consolidates email, calendar appointments, and task assignments in a single interface. Shared mailboxes and folder structures can be used to coordinate client correspondence across multiple stakeholders. Categorization tools enable basic segmentation of communications by project or priority. However, Outlook does not support relational linking of communications to structured data entities such as opportunities or contracts.
Excel remains a popular choice for tracking client data due to its accessibility and versatility. Structured tables and formulas allow teams to capture client information, track opportunities, and monitor revenue projections. Pivot tables and charts can generate simple reporting views to support decision-making. Despite these strengths, Excel introduces risks related to data consistency and access control. Performance constraints also emerge when managing large datasets or complex relationships.
SharePoint supports structured document management and collaboration. Libraries can be configured with metadata, versioning, and permissions to control access to sensitive materials. Integration with Outlook and Teams simplifies file sharing and collaborative editing. SharePoint search capabilities improve the retrieval of contracts, proposals, and related documents. Nonetheless, SharePoint lacks the structured data models that define modern CRM systems.
Microsoft Access and Dataverse and provide relational data capabilities beyond Excel’s limitations. Access offers table relationships and form interfaces suitable for structured record-keeping in small environments. Dataverse delivers enterprise-grade scalability and security with built-in integration to Power Apps and Power Automate. These platforms enable more sophisticated client data management when configured effectively. However, building and sustaining them requires specialized expertise.
Power Automate supports the automation of workflows across the Microsoft ecosystem. For example, new client records can trigger notifications, task assignments, or document generation. Power BI transforms disparate data sources into interactive dashboards for performance monitoring. These tools improve visibility and reduce manual effort, but they require disciplined configuration and data governance. The effectiveness of automation and analytics depends on the underlying integrity of data structures.
Microsoft Office often provides a cost-effective foundation for organizations seeking basic client management capabilities. Existing Office 365 subscriptions include access to core tools such as Outlook, Excel, and SharePoint without additional licensing fees. This affordability appeals to small and mid-sized firms operating with limited budgets. Cost savings can be redirected toward training, process design, or incremental technology enhancements. While the initial investment is low, hidden expenses related to customization and long-term maintenance should be carefully evaluated.
Teams are already familiar with Microsoft Office applications, which reduces the need for extensive training. Familiarity increases user confidence and accelerates adoption of new workflows built within the Office environment. Employees can leverage existing knowledge to configure spreadsheets, manage documents, and track communications. This familiarity often results in fewer barriers to early implementation compared to introducing an unfamiliar CRM platform. Over time, training may still be necessary to address complexity and reinforce consistent practices.
Microsoft Office offers a high degree of flexibility in designing custom data models. Excel enables organizations to create unique fields, formulas, and conditional formatting tailored to business requirements. SharePoint supports document libraries with configurable metadata and access controls. Access and Dataverse expand capabilities further by introducing relational data structures and enterprise security features. This adaptability benefits firms with specialized workflows or evolving processes. Flexibility must be balanced with governance to prevent fragmentation.
Microsoft’s ecosystem is designed to interconnect seamlessly across Office, Azure, and the Power Platform. Azure Active Directory provides a central identity management framework for authentication and authorization. Power Automate and Power BI extend the core tools with workflow automation and analytics, enabling more streamlined operations. Integration with Teams facilitates real-time collaboration and document sharing. This interoperability reduces duplication and improves efficiency across departments. Proper configuration is necessary to ensure that integrations remain consistent and secure.
Office can be effective in environments where client engagement models are relatively simple and data volumes remain manageable. Professional service teams with a limited number of clients and low transaction frequency may achieve acceptable results with Excel and SharePoint. Document-centric workflows can be effectively managed using SharePoint’s collaboration features. Organizations without stringent regulatory requirements may not need the advanced compliance controls of dedicated CRM platforms. These scenarios illustrate where Office can deliver practical value with careful configuration and oversight.
Scalability challenges represent one of the most significant limitations of Microsoft Office for client relationship management. Excel is not engineered to support large datasets or simultaneous multi-user editing at high volumes. SharePoint performance can degrade as lists grow beyond recommended thresholds. Access databases can encounter stability issues when scaled beyond modest record counts. As organizations expand client portfolios, these constraints can lead to errors, data corruption, or system downtime. Anticipating growth requirements is critical to avoid operational disruption.
Using multiple Office tools to manage client data introduces fragmentation risks. Teams may store information in separate Excel files, SharePoint libraries, and Outlook folders, creating parallel data sets that lack alignment. Data silos complicate reporting and hinder consistent client communication. Reconciliation becomes a time-consuming manual task that diverts resources from higher-value activities. Fragmentation also increases the likelihood of inconsistencies and reduces confidence in reporting outputs. Centralized governance frameworks are necessary to maintain data integrity.
Organizations operating under regulatory frameworks face challenges in meeting compliance standards with Office alone. Dedicated CRM platforms provide built-in audit trails, consent tracking, and automated retention policies. Microsoft Office requires additional configuration and manual oversight to achieve similar outcomes. This approach increases administrative burden and creates risk exposure if processes are not followed consistently. Failure to demonstrate compliance can result in fines, reputational damage, and client trust erosion. Investing in clear policies and technical controls is essential.
Manual workflows built on Office applications are often inconsistent across teams and projects. Without standardized naming conventions and procedures, employees develop divergent practices that reduce efficiency. Inconsistencies complicate onboarding and create confusion when responsibilities shift among staff. Automation can mitigate some variation, but clear definitions and governance are needed to enforce compliance. Over time, a lack of process discipline undermines confidence in the system and drives workarounds. Sustainable operations depend on maintaining structured workflows.
Building a CRM client relationship management system with Office requires substantial manual setup. Custom lists, templates, and workflows must be designed, implemented, and maintained over time. Dependencies across applications increase the complexity of troubleshooting when issues arise. Without rigorous documentation and training, institutional knowledge becomes concentrated among a few individuals, introducing key-person risk. Managing manual configurations consumes time and can divert resources from strategic initiatives. Long-term sustainability relies on proactive planning and dedicated support capacity.
Feature comparisons highlight substantial differences between Microsoft Office and dedicated CRM platforms. Dedicated systems such as Dynamics 365, Salesforce, and HubSpot offer preconfigured entities, workflows, and compliance controls. In contrast, Office requires manual construction of relational data models and process automation. Reporting and analytics are more robust in dedicated solutions, with predictive scoring and AI-driven insights integrated out of the box. Dedicated platforms also include role-based security frameworks purpose-built for CRM scenarios. These differences are critical considerations for organizations evaluating technology investments.
Dedicated CRM software delivers capabilities that Office cannot easily replicate. These systems provide unified client records with configurable relationships among contacts, opportunities, and support cases. Advanced automation reduces manual effort and improves response times. Embedded compliance features support regulatory adherence without requiring extensive customization. Predictive analytics and AI recommendations improve decision-making and client engagement. These strengths align closely with modern expectations for client management excellence.
Total cost of ownership extends beyond licensing fees to include configuration, maintenance, training, and support costs. Office may appear less expensive initially, but hidden expenses can accrue over time as complexity increases. Dedicated CRM platforms often require higher upfront investment but deliver lower operational costs through automation and standardization. Organizations should evaluate costs over a multi-year horizon to understand the full financial impact. Careful analysis ensures that decisions align with both budget constraints and strategic objectives.
Office-based CRM configurations can succeed for specific use cases, but sustainability is a challenge as business demands evolve. Growth in client volumes, team size, and regulatory requirements increases the pressure on manual processes. Without scalable infrastructure, organizations risk performance bottlenecks and data fragmentation. Long-term success depends on the ability to adapt workflows and maintain data integrity. Evaluating sustainability early reduces the likelihood of reactive migrations later.
Selecting the best CRM for client management requires a structured assessment of organizational needs and capabilities. Evaluation criteria should include data volume expectations, workflow complexity, compliance obligations, and integration requirements. Teams must consider digital maturity and readiness to adopt new technology. Future scalability and alignment with strategic growth plans are also critical factors. These criteria help ensure that the chosen solution delivers consistent value over time.
Adoption plays a central role in determining the effectiveness of any client management system. Even the most sophisticated platforms cannot deliver value if teams fail to integrate them into daily workflows. Consistent usage ensures data accuracy, supports reporting, and reinforces standardized processes. Adoption requires clear communication of benefits, accessible training resources, and ongoing reinforcement. Organizations that prioritize adoption early are more likely to realize the full return on investment from their CRM initiatives.
Embedding process guidance within daily workflows improves consistency and reduces reliance on institutional memory. Visual cues, templates, and checklists can help employees complete tasks correctly without referring to external documentation. Automated reminders and task assignments further encourage adherence to defined processes. Integrating guidance into familiar tools such as Outlook and SharePoint reduces friction and promotes compliance. This approach supports operational excellence by reinforcing best practices at the point of action.
User engagement metrics provide insight into adoption levels and highlight areas needing additional support. Tracking login frequency, feature utilization, and data quality helps identify teams that may require targeted training. Regular reporting on engagement fosters accountability and encourages consistent participation. Feedback loops enable continuous improvement by capturing user perspectives and addressing pain points. Sustained engagement ensures that the client relationship management system remains a reliable foundation for business operations.
Continuous improvement is essential to adapt workflows as client expectations and regulatory environments evolve. Establishing regular review cycles ensures that processes remain efficient and aligned with organizational goals. Employee feedback can uncover opportunities to streamline tasks and reduce complexity. Process updates should be communicated clearly and reinforced through training and documentation. A culture of continuous improvement drives innovation and maintains competitiveness. Organizations committed to refinement are better equipped to respond to change.
CRM strategies must align with broader digital transformation objectives to maximize impact. Integration with other business systems creates a cohesive technology ecosystem that supports seamless client engagement. Data-driven insights enable more informed strategic decisions and improve responsiveness to market shifts. Automation reduces manual effort, freeing resources for higher-value activities. Clear alignment ensures that CRM initiatives contribute to overall organizational resilience and growth. Strategic cohesion strengthens the case for sustained investment in client management capabilities.
Technical strategies play a vital role in reducing the risks associated with Office-based CRM configurations. Implementing version control and data validation rules improves data integrity. Consolidating critical information into centralized repositories reduces duplication and fragmentation. Regular backups and disaster recovery planning protect against data loss and system failures. Clear documentation of technical architecture supports troubleshooting and maintenance. These measures create a more stable foundation for client management processes.
Strong governance is essential to maintain consistent data quality and process adherence. Defining ownership roles clarifies responsibilities for data stewardship and compliance oversight. Establishing naming conventions and metadata standards ensures uniformity across records and documents. Regular audits identify discrepancies and support continuous improvement. Governance frameworks also provide a basis for enforcing security and access policies. Structured governance builds confidence in the reliability of client information.
Ongoing training and support are critical to sustaining effective use of client management tools. Comprehensive onboarding programs introduce employees to workflows, data structures, and compliance requirements. Refresher training sessions reinforce key concepts and accommodate new hires or role changes. Accessible support resources, such as knowledge bases and help desks, empower users to resolve issues independently. Proactive communication keeps teams informed about updates and best practices. Investment in training contributes to long-term system success.
Effective change management mitigates resistance and accelerates adoption of new processes. Clear communication of project goals and expected benefits sets the stage for engagement. Involving stakeholders early in planning fosters buy-in and reduces uncertainty. Piloting workflows with select teams enables refinement before wider deployment. Regular progress updates and success stories reinforce momentum and build confidence. Structured change management creates a smoother transition to improved client relationship management practices.
Developing a roadmap for future enhancements provides direction and supports strategic alignment. Roadmaps should outline planned upgrades, integration initiatives, and process improvements. Prioritizing enhancements based on business impact ensures that resources focus on the most valuable opportunities. Regularly revisiting the roadmap keeps plans relevant as organizational needs evolve. Transparency about timelines and milestones fosters accountability and shared understanding. A clear roadmap positions the organization for long-term success.
Evaluating operational complexity is a crucial first step in determining whether Office can serve as a viable CRM. Organizations with simple, transactional engagement models may find Office sufficient for managing client relationships. Complex workflows involving multiple departments and high transaction volumes often exceed the platform’s practical limitations. Detailed mapping of processes and data flows clarifies where Office meets requirements and where gaps remain. A structured assessment reduces the risk of unexpected challenges during implementation.
Compliance considerations are paramount when assessing CRM options. Industries subject to stringent regulations must demonstrate control over data access, retention, and processing activities. Dedicated CRM platforms include built-in features that simplify compliance with frameworks such as GDPR and HIPAA. The office requires manual configuration and disciplined oversight to achieve similar outcomes. Evaluating the feasibility of meeting compliance obligations informs whether Office is an appropriate long-term solution. Clear understanding of requirements supports informed decision-making.
Growth projections should inform CRM platform selection to avoid scalability constraints. As client volumes increase, Excel and SharePoint performance can degrade, creating operational bottlenecks. Additional team members introduce complexity in maintaining consistent workflows and data integrity. Anticipating growth enables proactive planning for infrastructure, process standardization, and training needs. Evaluating scalability early reduces the likelihood of reactive migrations as business demands evolve. Forward-looking strategies help sustain operational effectiveness.
Digital maturity influences an organization’s ability to maintain a CRM built on Office. Teams with experience managing complex configurations are better positioned to address the challenges of customization and governance. Organizations with limited technical resources may struggle to sustain manual workflows and integrations. Assessing readiness ensures that support structures and skill sets align with system requirements. Digital maturity assessments identify gaps that can be addressed through training or targeted investments. Readiness evaluation strengthens implementation planning and risk management.
Short-term cost savings are often a compelling reason to adopt Office as a CRM. However, balancing immediate benefits against long-term sustainability is critical. Organizations should consider how workflows, compliance requirements, and data volumes will evolve over time. Dedicated CRM platforms may offer higher upfront costs but deliver greater scalability and efficiency. Aligning platform selection with strategic goals ensures that investments support future growth and resilience. Thoughtful planning minimizes disruption and maximizes return on investment.
Artificial intelligence will continue to shape the CRM landscape over the next decade. Predictive analytics will become more sophisticated, enabling accurate forecasting of client behavior and revenue trends. Machine learning models will identify patterns and recommend actions to improve engagement outcomes. Natural language processing will streamline information retrieval and reporting. These advancements will drive higher productivity and more personalized client interactions. Organizations that embrace AI will be better equipped to compete in dynamic markets.
Conversational interfaces are transforming how professionals interact with CRM systems. Voice assistants and chatbots will allow users to query data and perform tasks without navigating complex menus. These interfaces improve accessibility and reduce reliance on specialized training. Integration with other enterprise systems will create seamless workflows spanning multiple platforms. As adoption increases, conversational tools will become an expected feature of modern CRM solutions. Their impact on user experience and efficiency will be significant.
Automation will continue to expand across every aspect of client relationship management. Workflows that once required manual intervention will become fully automated, improving speed and consistency. Automated alerts and follow-up sequences will ensure that no client interactions are overlooked. Data entry tasks will diminish as systems capture information directly from communications and transactions. Higher automation levels will reduce operational costs and free capacity for strategic initiatives. Meeting these expectations requires platforms that support advanced workflow design.
Predictive relationship management represents the next evolution in CRM capabilities. Systems will analyze behavioral data to anticipate client needs and tailor outreach accordingly. This proactive approach strengthens client loyalty and increases conversion rates. Predictive insights will also inform resource allocation and performance optimization. Organizations that build data-driven cultures will extract greater value from predictive tools. Preparing for this shift involves investing in data quality and analytics readiness.
Several trends will continue to shape CRM systems in the years ahead. Cloud-native architectures will become the standard for scalability and accessibility. Low-code development will empower business users to customize workflows without relying on IT resources. Integration with external data sources will create richer client profiles and deeper insights. Emphasis on privacy and security will drive innovations in compliance management. These trends reinforce the need for flexible, forward-looking CRM strategies.

In my experience advising organizations of all sizes, I have found that Microsoft Office can function as a practical CRM for client management under certain conditions. For smaller teams with straightforward engagement models, Office offers a familiar, cost-effective environment to track relationships and collaborate without introducing new systems. However, I have also seen firsthand how quickly its limitations emerge as complexity and scale increase.
When client data starts to multiply or regulatory requirements tighten, relying exclusively on Excel, SharePoint, and Outlook often becomes unsustainable. Fragmented information, inconsistent processes, and manual workarounds create risks that can undermine trust in the system and frustrate teams. I have worked with firms that underestimated these challenges and later faced expensive migrations and prolonged adoption hurdles.
Ultimately, success comes down to clarity and commitment. If you decide to leverage Office as your primary client relationship management system, you must invest in thoughtful configuration, governance, and training. If your growth ambitions or compliance obligations demand more advanced capabilities, I recommend evaluating purpose-built CRM platforms early in your planning process.
Whatever path you choose, the most crucial step is to approach this decision with a structured framework and a long-term perspective. When organizations align technology with strategy, assign clear ownership, and prioritize continuous improvement, they build not only a better CRM but also a foundation for stronger client relationships and sustainable growth.
At VisualSP, we understand that selecting and implementing a client relationship management system is only part of the journey. Even the most advanced CRM or Microsoft Office configuration cannot deliver lasting value if teams struggle to adopt the tools or follow consistent processes. That is why we built VisualSP to provide real-time, contextual support that empowers users exactly when and where they need help.
Our platform integrates seamlessly into your Microsoft 365 environment, including SharePoint, Teams, and Outlook, so you can guide employees through workflows without requiring them to leave the applications they already use. VisualSP delivers in-context walkthroughs, inline help, videos, and AI-generated guidance that accelerates user adoption and reinforces best practices. For organizations relying on Microsoft Office for client management, our solution reduces the risk of data inconsistencies and improves productivity by giving everyone clear, on-screen instructions.
VisualSP also offers an AI-powered assistant that helps your team work more efficiently. From generating prompt templates to automating repetitive tasks like summarizing emails and extracting CRM data, our AI tools simplify complex processes and ensure employees stay focused on high-value work. With enterprise-grade security and a user-friendly interface, VisualSP makes it easier than ever to drive adoption, maintain compliance, and scale your digital transformation initiatives.
If you are considering ways to improve the effectiveness of your Microsoft client relationship management strategy or are planning a transition to a dedicated CRM platform, VisualSP can help you get there faster.
Fuel Employee Success
Stop Pissing Off Your Software Users! There's a Better Way...
VisualSP makes in-app guidance simple.